Building Java Programs
Lab: ArrayLists
Except where otherwise noted, the contents of this document are Copyright 2019 Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp.
Lab goals
Goals for this problem set:
- Gain familiarity using Java's
ArrayListcollection - Use Java's type parameters (generics)
- Practice traversing lists and examining their elements
- Practice inserting and removing from the front, middle, and end of a list
ArrayList
ArrayList: Stores an ordered sequence of elements using an array as its internal data structure.
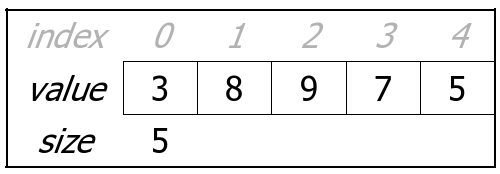
- each element is accessible by a 0-based index
- a list has a size (number of elements that have been added)
- elements can be added to the front, back, or elsewhere
ArrayList Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
list.add(value); |
appends value at end of list |
list.add(index, value); |
inserts given value just before the given index, shifting subsequent values to the right |
list.clear(); |
removes all elements of the list |
list.get(index) |
returns the value at given index |
list.indexOf(value) |
returns first index where given value is found in list (-1 if not found) |
list.remove(index); |
removes/returns value at given index, shifting subsequent values to the left |
list.set(index, value); |
replaces value at given index with given value |
list.size() |
returns the number of elements in list |
list.toString() |
returns a string representation of the list such as "[3, 42, -7, 15]" |
Exercise : ArrayList declaration syntax

Which of the following choices is the correct syntax for declaring/initializing an ArrayList of integers?
Exercise : mystery

Write the output produced when passing each ArrayList to the following method:
public static void mystery(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += 2) {
int element = list.get(i);
list.remove(i);
list.add(element);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
[2, 4, 6, 8] // [4, 6, 2, 8] [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60] // [20, 30, 50, 60, 40, 10] [-4, 16, 9, 1, 64, 25, 36, 4, 49] // [16, 9, 64, 25, 4, 49, 1, 36, -4]
Exercise : mystery2

Write the output produced when passing each ArrayList to the following method:
public static void mystery2(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
list.add(list.get(i));
} else {
list.add(0, list.get(i));
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
[10, 20, 30] // [20, 10, 20, 30, 30, 20] [8, 2, 9, 7, 4] // [8, 7, 8, 2, 9, 7, 4, 4, 2, 8] [-1, 3, 28, 17, 9, 33] // [33, 28, 33, -1, 3, 28, 17, 9, 33, 17, -1, 33]
Exercise : Debugger
-
 PluralWords.java
PluralWords.java
-
Set a breakpoint on the
ifstatement inside theforloop (line 14).
Your editor's debugger can be helpful to see the state of ArrayLists in a running program.
Download the following PluralWords program and run it in the debugger.
continued on the next slide...
Exercise - Debugger
-
Now you can debug the program by clicking on the debug icon
 (looks like a ladybug).
(looks like a ladybug).
-
It will stop every time it hits line 14.
Then you can see the values of variables
i,word, andallWords. - To continue running, press the buttons in your editor to Continue or Step.
-
Using this approach, fill in the table below indicating what value
wordhas whenihas the given value. (Don't forget to surround the value with""quotes.) Keep in mind that you are figuring out what valuewordhas just before it executes this line of code.i = 0, word ="I"
i = 1, word ="love"
i = 2, word ="foxes"
i = 3, word ="cats"
i = 4, word ="puppies"
i = 5, word ="and"
Can you figure out the bug in the program?
Modify the code so that it will remove ALL words that end in "s".
Recall: ArrayList as Parameter
public static void name(ArrayList<Type> name) {
Example:
// Prints all plural words from the given list.
public static void printPlural(ArrayList<String> list) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String str = list.get(i);
if (str.endsWith("s")) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
Exercise : acronymFor

Write a method called acronymFor that takes an ArrayList of strings as a parameter and that returns an acronym made by combining the capitalized first letter of each word in the list.
For example, the list [laughing, out, loud] produces the acronym "LOL".
Exercise : addStars
Write a method called addStars that accepts an ArrayList of strings as a parameter and places a "*" after each element.
For example, if an list initially stores [the, quick, brown, fox], you should modify it to store [the, *, quick, *, brown, *, fox, *].
Exercise : switchPairs

Write a method called switchPairs that switches the order of values in an ArrayList of strings in a pairwise fashion.
Your method should switch the order of the first two values, then switch the order of the next two, switch the order of the next two, and so on.
If there are an odd number of values in the list, the final element is not moved.
For example, if a list stores [to, be, or, not, to, be, hamlet], you should modify it to store [be, to, not, or, be, to, hamlet].
Exercise : reverse3

Write a method called reverse3 that accepts an ArrayList of integer values as a parameter and that reverses each successive sequence of three values in the list.
If the list has extra values that are not part of a sequence of three, those values are unchanged.
For example, the list:
[3, 8, 19, 42, 7, 26, 19, -8, 193, 204, 6, -4]
should be modified to store:
[19, 8, 3, 26, 7, 42, 193, -8, 19, -4, 6, 204]
Exercise : intersect

Write a method called intersect that accepts two sorted ArrayLists of integers as parameters and returns a new list that contains only the elements that are found in both lists.
For example, if lists named list1 and list2 initially store:
[1, 4, 8, 9, 11, 15, 17, 28, 41, 59][4, 7, 11, 17, 19, 20, 23, 28, 37, 59, 81]
Then the call of intersect(list1, list2) returns the new list:
[4, 11, 17, 28, 59]